If you are an email user, you might have dealt with spam. It is the necessary evil that plagues our mailboxes. There are all kinds of phishing and scammy emails that years are prone to click on, resulting in the harm caused to you and/or your device.
But has it occurred to you how spam emails are differentiated from authentic emails?
With the help of an authentication technique called Sender Policy Framework or SPF.
What does Sender Policy Framework (SPF) mean?
SPF identifies legitimate emails and fake ones by linking an email to a domain. It prevents spammers from sending spam emails on behalf of the domain.
Why is an SPF important?
Because the inability to identify authentic emails is a huge flaw that results in spam.
Spam includes inaccurate, irrelevant, or fake emails. Fake emails are emails that are sent from illegitimate or unauthenticated sources. To authenticate an email, the sender must register with the corresponding domain to be able to send out legitimate emails.
Needless to say, SPF comes with a host of benefits like
- Increasing domain visibility
- Shielding from domain impersonation and email spoofing
- Improving email deliverability
- Bolstering email marketing
Without SPF and other authentication technologies, we would drown in an ocean of spam, unverified emails, and all kinds of bloatware.
How does SPF work?
SPF requires the domain owner, aka the email sender, to submit a list of records to the ISP (Internet Service Provider).
This list contains a bunch of acceptable IP addresses waiting to be verified by the DNS, which is a universally global database where people, as well as computers, go to find out information on websites and domains.
A link between the domain and the email is established upon successful publication.
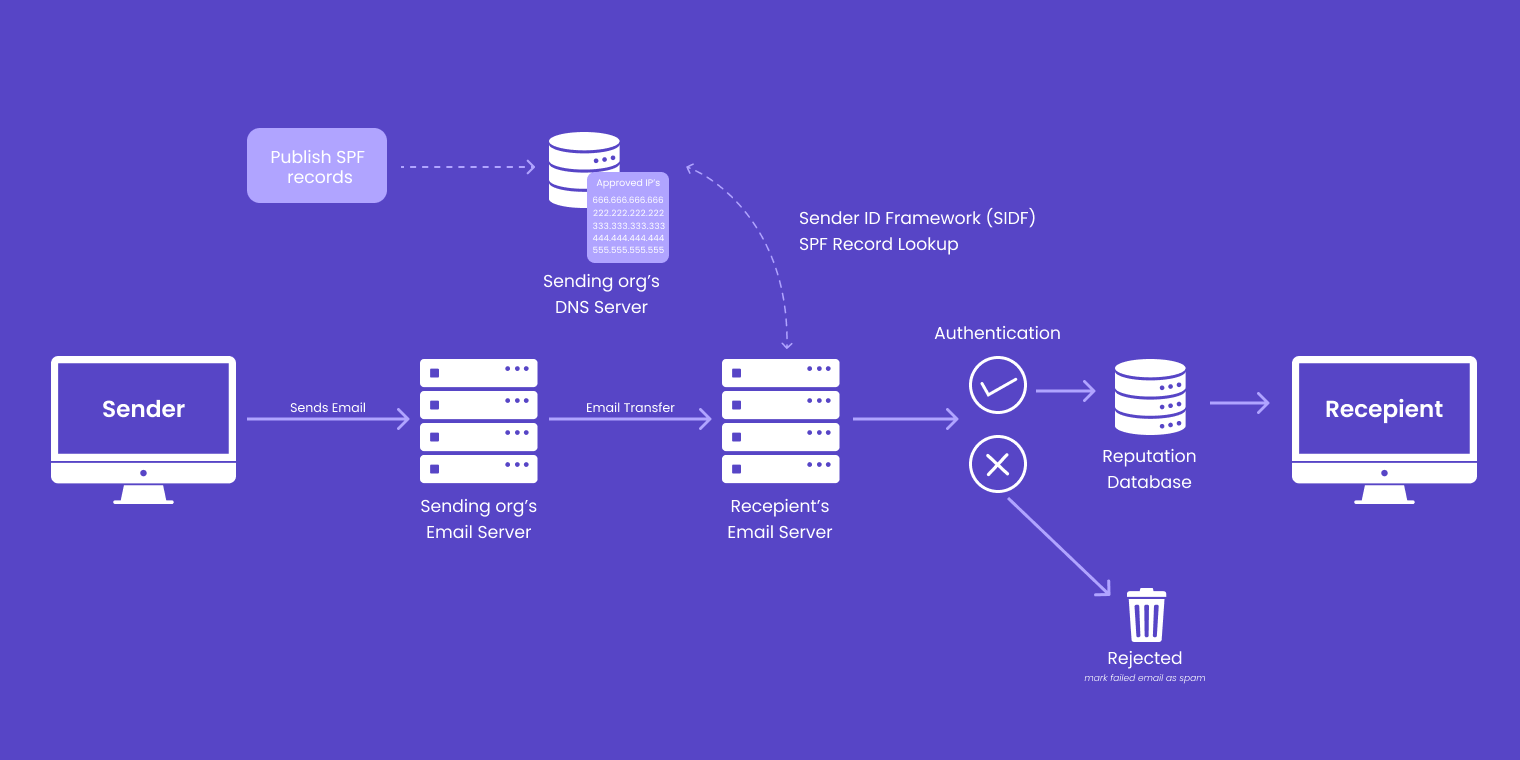
When that domain owner sends an email, the recipient’s mail server checks the list of allowed senders. If this check is approved, it is successfully delivered, and if rejected, it is marked as spam.
SPF is just one of many email authentication frameworks. According to DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance), there are other frameworks just like it, a governing authority/protocol on email best practices.
For example, DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail) is another standard authentication method used to prevent emails from malicious hacks like spoofing and phishing by implementing cryptography.
DKIM and SPF, although mutually exclusive, serve similar purposes and must coexist parallelly for spam as well as security management.
Conclusion
Simply put, Sender Policy Framework is a free authentication technology that tells us which emails are real and which ones aren’t by getting the email senders verified so they can send emails that won’t end up as spam. Without SPF and other authentication technologies, we would drown in an ocean of spam, unverified emails, and all kinds of bloatware.