The telecommunications industry is a behemoth that supports the foundation of contemporary communication and network infrastructure. The significance of the telecom industry is growing with the globalization of our society. However, finding and keeping customers is a major challenge for telecom companies in this era of intense competition and rapid technological advancements.
The success of telecom companies now hinges on two previously unanticipated factors: customer acquisition and customer retention. For any business to expand, customer retention is just as crucial as bringing in new customers. In this dynamic setting, segmentation and personalization have proven crucial.
Segmentation, the process of dividing customers into groups with similar characteristics, helps telecommunications companies better target their products and services. It allows for individualized plans to be developed, increasing the likelihood that the intended consumers will be reached through advertising. In this quest, personalization plays a pivotal role by catering to each customer’s specific likes, dislikes, and other preferences.
The telecom industry is ripe for segmentation and personalization, and we’ll be exploring those areas here. The various elements of these strategies, as well as their effects on new and returning customers, as well as the main difficulties and potential gains associated with them will be discussed. Come along as we explore the tactics that have helped telecom companies succeed in today’s interconnected world.
Understanding Segmentation
Segmentation, at its core, is the process of categorizing a diverse customer base into distinct groups based on shared characteristics and behaviors. In the telecom industry, this strategic approach is instrumental in understanding and effectively catering to the unique needs and preferences of customers. Let’s delve deeper into the concept of segmentation, its various types, and the advantages it offers.
Types of Customer Segmentation for Telecom
- Usage-Based Segmentation: Telecom companies can segment customers based on their usage patterns. This includes data usage, call duration, text message volume, and app usage. This segmentation helps tailor service plans, ensuring customers have the right amount of data or minutes to fit their needs.
- Customer Value Segmentation: This model divides customers based on their lifetime value to the telecom provider. High-value customers who consistently subscribe to premium plans may receive exclusive offers or personalized customer support, while cost-conscious customers may be offered more budget-friendly options.
- Bundling Behavior Segmentation: This model looks at customer preferences for bundled services. Some customers prefer all-in-one packages that include internet, TV, and phone services, while others may only want one specific service. Telecom companies can segment and offer tailored bundle options.
- Contract Length Segmentation: Segmenting customers by their contract lengths (e.g., month-to-month, annual contracts) allows telecom providers to customize retention strategies. Customers nearing the end of their contracts may receive renewal incentives, while those on month-to-month plans may receive special offers to encourage longer commitments.
Benefits of Effective Segmentation for Telecom
- Churn Reduction: Segmentation helps identify high-risk customers who are more likely to switch to a competitor. Telecom companies can implement targeted retention strategies for these segments, offering incentives or personalized solutions to reduce churn rates.
- Customized Pricing: Telecom providers can use segmentation to create customized pricing models. For instance, they can offer tiered data plans based on usage patterns, ensuring that heavy data users get cost-effective plans while light users pay less.
- Service Expansion: Telecoms can use segmentation to identify underserved or unsaturated markets. By understanding the unique needs and preferences of these segments, they can launch targeted marketing campaigns and service expansion efforts to capture new customer segments.
In the telecom industry, segmentation serves as the foundation upon which personalization efforts are built. It’s a strategic tool that enables providers to navigate the complex landscape of customer acquisition and retention effectively. In the sections that follow, we will explore how personalization complements segmentation to create a winning strategy for telecom companies.
The Power of Personalization
One of the keys to attracting and retaining customers in the fiercely competitive telecom industry lies in the field of personalization. Personalizing customer service and interactions to each customer’s unique needs and habits can make a huge difference. Here, we’ll define “personalization” in the context of telecommunications, explain how it differs from “customization,” and look at some concrete examples of its use.
The concept of personalization in the telecommunications industry refers to the process of designing experiences that are specific to each individual customer and their preferences, habits, and requirements. The key is to avoid a generic approach and instead provide services and content that speak directly to the individual. This can include anything from a customer’s service plan to their content recommendations and marketing efforts in the telecommunications industry.
Personalization vs. Customization in Telecom
While both personalization and customization aim to provide customers with unique experiences, they take very different approaches to doing so.
Data-driven insights are the backbone of the personalization process, which aims to automatically satisfy customers’ wants and needs. For instance, if a customer consistently goes over their data limit, you may want to recommend that they upgrade their plan.
In contrast, allowing customers to tailor their experience by selecting individual features and setting their own preferences is at the heart of customization. Customers could, for example, tailor their own TV channel bundles and select from a la carte add-ons.
Examples of Personalization in the Telecom Industry
- Tailored Service Plans: Telecom providers can analyze a customer’s usage patterns and preferences to offer personalized service plans. For instance, if a customer primarily uses their phone for data-heavy applications like streaming, a plan with unlimited data or high data caps could be recommended.
- Family and Group Plans: Telecom providers can use personalization to facilitate the creation of family or group plans. By understanding the relationships and usage patterns among family members or group users, providers can offer customized plans that cater to their collective needs while ensuring cost savings.
- Data Management Tools: Personalization can extend to data management tools, where customers have the ability to personalize their data usage limits or preferences. For example, they can adjust data caps based on their needs, allowing for flexibility in their plans.
Personalized service is about more than just making a customer feel appreciated; it’s also about meeting their actual needs. This level of individualization has the potential to increase customer retention, satisfaction, and revenue. In what follows, we’ll examine how the telecom industry can benefit from combining segmentation and personalization to better attract and keep customers.
The Customer Lifecycle in Telecom
In the telecommunications sector, customer lifecycle management is of paramount importance. Acquiring new customers, activating them, and keeping them engaged over time are all part of the same journey. The importance of segmentation and personalization in creating a positive experience for the customer will be discussed in detail.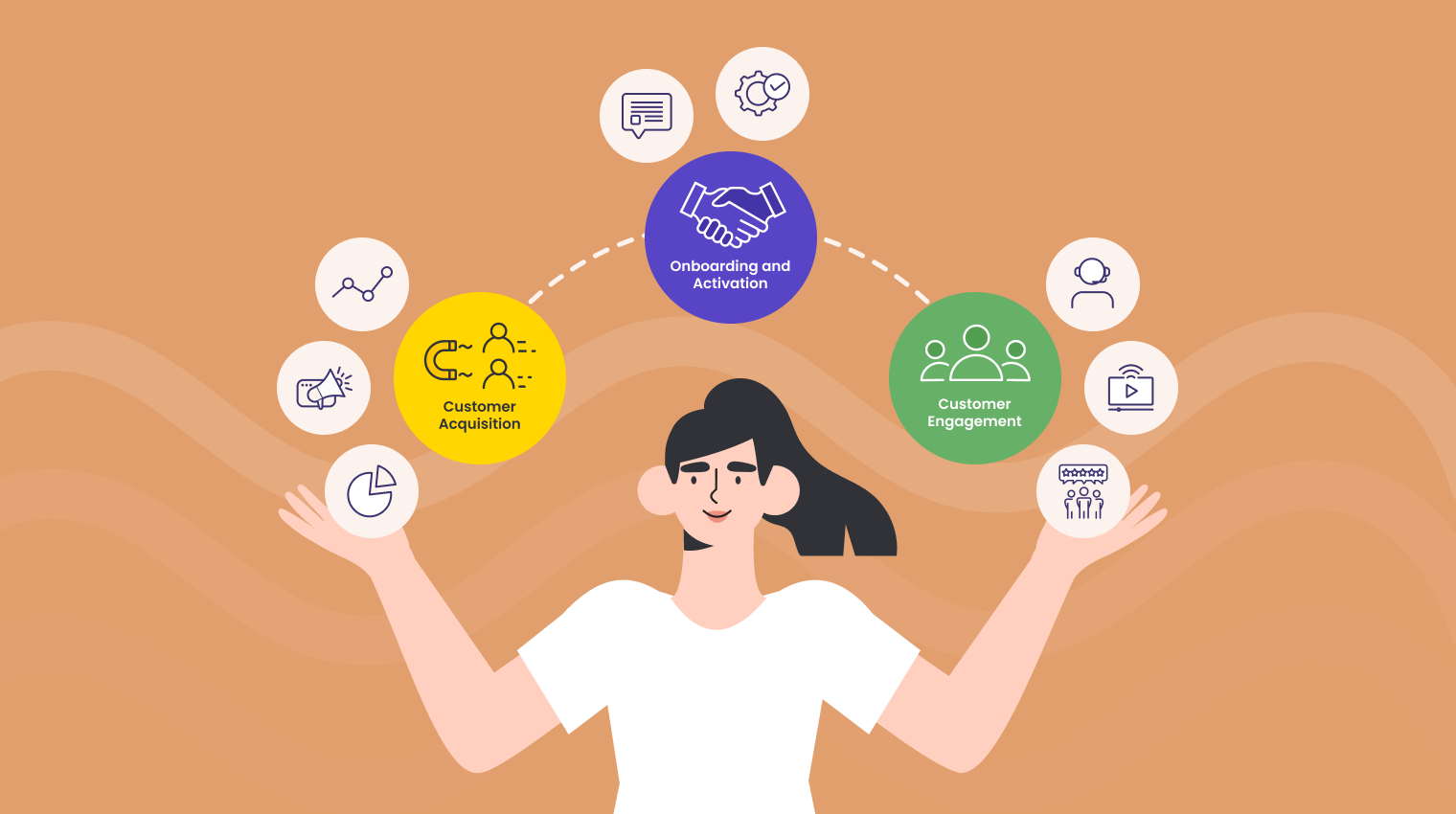
Customer Acquisition
- Identifying Target Segments: Identifying target markets is a crucial first step for telecom companies when expanding their customer base. As was previously mentioned, segmentation strategies enable providers to identify high-growth, high-retention subsets of their customer base. Depending on their business strategy, a telecom provider may focus on specific customer groups, such as “young professionals seeking affordable data plans” or “families needing comprehensive communication packages.”
- Crafting Compelling Offers: Insights gained from segmentation are priceless when developing alluring promotional offers. The identified segments can then be targeted with specific service packages, advertising campaigns, and price points. For the “entertainment-focused” market, a telecommunications company may package high-speed internet, unlimited calling, and streaming subscriptions.
- Utilizing Data Analytics: Data analytics is a powerful tool for customer acquisition. By analyzing data related to customer acquisition channels, telecom companies can determine which marketing efforts are most effective for each segment. This data-driven approach allows for efficient allocation of marketing resources and the ability to refine strategies over time.
Onboarding and Activation
- Personalized Welcome Messages: The customer’s journey pivots at the onboarding and activation stages. The transition can be easier and more memorable with the help of personalized welcome messages. If you really care about giving your customers a good experience, you should send them a message thanking them for selecting your service and highlighting the features that will be most useful to them.
- Seamless Setup Processes: The installation and activation procedures can be tailored to the individual. A customer who just bought a smartphone, for instance, may receive straightforward setup instructions and prompts for downloading the provider’s app. This kind of care can have a big impact on first impressions.
Customer Engagement
- Proactive Customer Support
Engagement can be increased through proactive customer support. Data-driven insights allow telecom companies to foresee and solve customer issues before they escalate. If a customer’s data consumption suddenly increases, for instance, the service provider may suggest an upgrade to prevent costly overage fees. - Loyalty Programs
Programs that reward repeat business and interest from new clients are called loyalty programs. Customer preferences and habits can be taken into account when designing a loyalty program. A customer who frequently travels internationally, for instance, might be eligible for special pricing on international data plans because of their loyalty.
The telecom customer lifecycle is an ongoing and ever-changing process that necessitates close monitoring at all times. Telecom companies can improve customer relationships, lower customer churn, and increase profits in a cutthroat market by using segmentation and personalization at every touchpoint.
Case Studies
Telecom Company Leveraging Segmentation
AT&T employs customer segmentation as a foundational strategy across various facets of its operations. This involves collecting and analyzing customer data, encompassing demographics, spending behaviors, and usage patterns, to construct comprehensive customer profiles. These profiles enable AT&T to gain insights into the unique needs and preferences of different customer segments.
These insights are then strategically applied to:
- Targeted Marketing and Sales: AT&T effectively tailors its marketing and sales efforts by leveraging customer segmentation. This means that specific customer segments, like millennials or older demographics, receive targeted advertising aligning with their preferences. For instance, millennials might be presented with data-heavy plans, while older customers receive ads for voice and messaging plans.
- Enhanced Customer Service: Customer segmentation plays a pivotal role in optimizing customer service. AT&T ensures that customer inquiries are routed to agents who possess the expertise and resources to address specific concerns. This approach enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of customer support.
- Informed Business Decisions: AT&T leverages customer segmentation to make informed business decisions. This extends to identifying emerging market opportunities and crafting new products and services that resonate with distinct customer segments.
Successful Personalization Initiatives
Verizon has achieved remarkable success through its comprehensive personalization initiatives:
- Verizon Digital CX: This suite of AI-driven tools empowers businesses to provide personalized customer experiences across all channels. These tools have notably reduced customer churn for businesses by up to 50%.
- Verizon Smart Rewards: Leveraging AI, this loyalty program tailors rewards based on customer spending habits, interests, and location. By delivering personalized offers and discounts, it has increased customer engagement by up to 20%.
- Verizon Media Platform: This suite of advertising solutions utilizes AI to deliver highly personalized ads to customers. By considering customer demographics, interests, and browsing history, it serves relevant and timely ads, resulting in an impressive 15% increase in ad revenue.
Verizon’s achievements serve as a compelling model for businesses seeking to enhance the customer experience. By harnessing AI to gather and interpret customer data, organizations can deliver experiences that are not only relevant and timely but also deeply engaging.
Challenges and Considerations
While Verizon and other forward-thinking companies have reaped many benefits from personalization initiatives, these endeavors are not without their fair share of challenges and considerations. These are fundamental for ensuring that personalization strategies are applied ethically and efficiently.
1. Data Privacy and Security
The fact that personalization depends on data collection and analysis raises concerns about customers’ privacy and security. Customers give their personal information to businesses, and it is crucial that this information is protected. Legal ramifications and a loss of trust can result from data breaches and privacy violations. Finding the sweet spot between user privacy and customization is a challenge worth taking on.
2. Balancing Personalization with Customer Privacy
While customers appreciate bespoke service, they are protective of their personal data. Finding an acceptable balance between the two is essential. Companies have a responsibility to be open and honest with their customers about the data they collect and how it will be used, give customers the option to participate in or decline personalization efforts, and keep customer information private and secure. It is a continuing challenge to achieve personalization without jeopardizing customers’ privacy.
3. Technology and Infrastructure
Strong technology and infrastructure are essential for launching successful personalization initiatives. Tools with AI functionality, data analytics platforms, and the capacity to process and analyze massive amounts of customer data in real time all fall under this category. These technological assets require continuous investment for maintenance and improvement.
4. Keeping Up with Changing Customer Preferences
It’s important to keep up with the shifting preferences and habits of your customers. Keeping tabs on these changes is crucial for keeping personalization efforts current and fruitful. Companies need to tweak and adjust their strategies frequently to meet the shifting demands of their customers.
To successfully navigate these factors, a proactive and customer-centric strategy is required. In order to fully capitalize on the benefits of personalization while minimizing the risks associated with it, businesses must place a premium on data security, transparency, and the changing wants and needs of their customers. Next, we’ll look at how to successfully launch and maintain a personalized service in the telecommunications sector.
Best Practices
Implementing and sustaining effective personalization in the telecom industry demands a strategic approach that encompasses best practices. These practices not only optimize the impact of personalization but also address the challenges and considerations we’ve previously discussed.
1. Data Collection and Analysis
Accurate and in-depth data collection and analysis is crucial for efficient personalization. In order to efficiently collect, process, and interpret customer data, telecom companies should invest in robust data analytics tools and methodologies. In order to provide timely individualized experiences, this also includes real-time analysis. Conduct thorough audits of your data collection processes on a regular basis to guarantee privacy and security.
2. Cross-Functional Collaboration
Personalization is not the sole responsibility of a single department; it requires collaboration across various functions within an organization. Marketing, customer service, IT, and data analytics teams must work in tandem to ensure a cohesive and consistent approach to personalization. Cross-functional teams can share insights and expertise to refine personalization strategies and deliver more comprehensive customer experiences.
3. Continuous Improvement
Customers’ tastes and technological capabilities are constantly shifting. Continuous improvement is necessary to ensure that personalization efforts continue to yield positive results. This requires a dedication to constant evaluation, experimentation, and modification. You should check in with your customers frequently to see how they’re responding to your personalization efforts and make adjustments based on what you learn. Telecommunications providers can maintain a competitive edge in the individualized services market by maintaining a nimble and adaptable business operation.
Telecom companies can fully realize the potential of personalization if they follow these best practices and overcome the difficulties presented by data privacy, technology, and shifting customer preferences.
Conclusion
In this exploration of segmentation and personalization in the telecom industry, we’ve unveiled a roadmap to enhance customer acquisition and retention. Let’s recap the key takeaways: We began by understanding the significance of segmentation, where customer groups are formed based on shared characteristics, and personalization, the art of tailoring experiences to individual preferences. The customer lifecycle in telecom involves acquisition, onboarding, and engagement, with each stage being an opportunity for segmentation and personalization.
We showcased how telecom giants like AT&T and Verizon have successfully harnessed these strategies to improve customer experiences and business outcomes. However, we also acknowledged the challenges, such as data privacy, technology infrastructure, and the ever-evolving customer landscape, that demand careful consideration in the pursuit of personalization excellence.
As we look ahead, the landscape of telecom customer management is evolving at a rapid pace, with emerging technologies like AI and 5G poised to transform the industry further. The path forward is clear: embracing segmentation and personalization is not merely a choice but a necessity for telecom companies seeking to thrive in a highly competitive market.
To explore the limitless possibilities of segmentation and personalization in telecom, book a demo with WebEngage, the leading retention marketing platform. Their expertise can revolutionize your efforts, ensuring your telecom company remains at the forefront of customer-centric strategies.
In this ever-connected world, where customer expectations continue to rise, segmentation and personalization stand as the compass guiding telecom companies toward sustained growth, loyalty, and unparalleled customer satisfaction.






 Harshita Lal
Harshita Lal
 Sharath Byloli
Sharath Byloli
 Ananya Nigam
Ananya Nigam
 Ajit Singh
Ajit Singh