No business has customers who are carbon copies of each other. And if your marketing efforts are not personalized to meet each customer’s unique persona, you’re missing out on extracting the maximum value from each customer. The answer? Customer segmentation.
Over 80% of modern consumers are more likely to purchase from brands that deliver a personalized experience. And customer segmentation is your safe route to delivering personalized interactions at scale.
Customer segmentation is the process of dividing customers based on shared commonalities. Doing so aids in streamlining your marketing, sales, and customer service campaigns to be personalized to meet each customer’s needs.
This article will show you how to segment your customers and improve your business.
8 ways in which businesses can and should segment customers
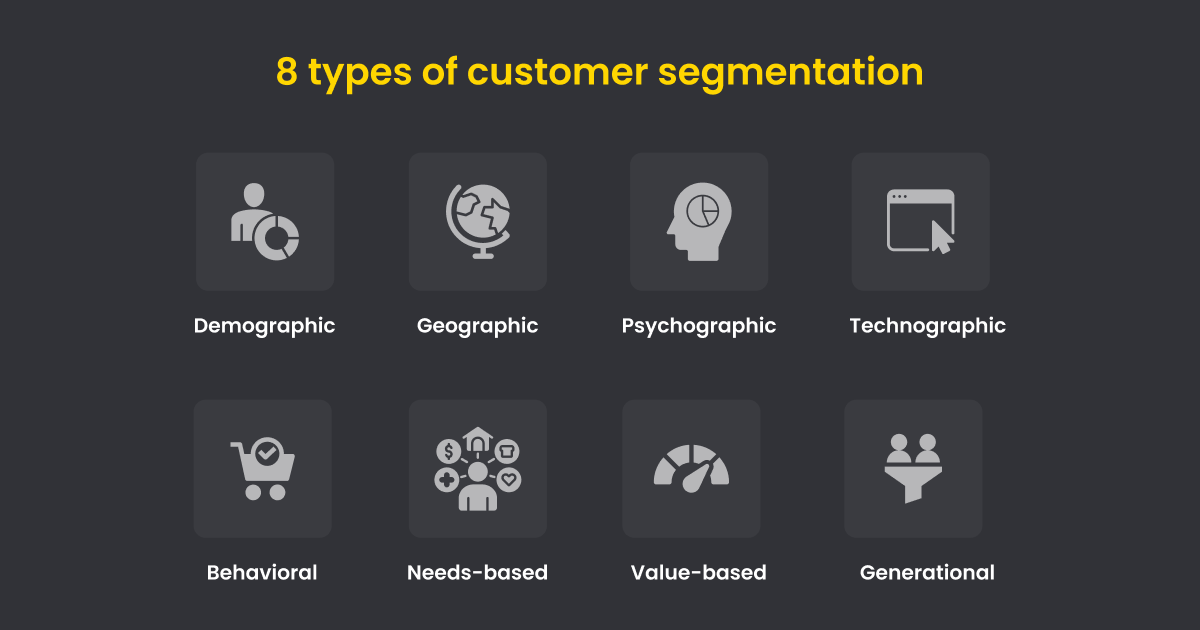
1. Demographic segmentation
Demographic segmentation is based on socioeconomic customer categories, such as gender, age, occupation, household income, and marital status.
Say you’re a luxury fashion brand. By targeting and segmenting high-income individuals from metropolitan cities, you could achieve better conversions by creating ads for your premium products.
2. Geographic segmentation
Geographic segmentation lets you group customers based on location, language, transportation, and workspace.
This type of segmentation is not limited to your customers’ physical locations like countries or cities. You can further segment your customers based on geographic variables like climatic conditions, food/clothing preferences, etc. Doing so lets you sell products or services to individuals who find your offerings useful.
A classic example of such geographic segmentation is winter wear. Months considered cold winters in western countries may not be the same for South-Asian countries. So a global brand would be running climate-specific ads for its winter collection.
3. Psychographic segmentation
Grouping customers based on their shared traits or mannerisms like values, interests, and personalities is termed psychographic segmentation.
For example, vegan food companies should target their marketing, ads, and sales campaigns for vegan or vegetarian audiences, which is only possible through psychographic segmentation.
4. Technographic segmentation
Businesses must know how their audience consumes content. Is it through a specific smartphone, browser, or other sources?
This method of grouping customers is known as technographic segmentation. It’s a deeper and more hyper-personalized segmentation that lets you understand customers based on their technology.
An example of technographic segmentation is when brands divide customers based on the browsers they use. Suppose you’re a brand selling iPhone cases. You can target users who use the Safari browser over Chrome.

5. Behavioral segmentation
In this segmentation, you group customers based on their purchase patterns, lifestyle, website activity, and last engagement.
Behavioral segmentation of customers lets you level up personalization strategies and send targeted email campaigns, run activity-focused ads, and understand purchase patterns. Another major benefit of this segmentation is understanding the awareness stage of each customer, for instance, if the customer is product-aware, solution-aware, and so on.
6. Needs-based segmentation
Segmenting users based on specific needs like product attributes, service needs, or delivery methods lets you execute hyper-focused marketing campaigns.
For instance, an energy drink brand can market to athletes, a baby clothing brand to new parents, or offer cash on delivery to senior customers.
7. Value-based segmentation
Value-based segmentation is understanding the economic value of your target audience and grouping them based on how much value they add to your business. One way to segment this is through customer satisfaction (CSAT) scores, number of purchases, and average purchase value.
Why is this important? Targeting such high-value customers lets you nurture them with the right promotional methods and turn them into brand loyalists.
8. Generational segmentation
Generational segmentation is a blend of behavioral and demographic segmentations, where you segment and market to customers based on their generation.
This form of segmentation hugely relies on the fact that customer buying patterns, preferences, and ideologies can be understood based on generations like Gen X, Gen Z, Millennials, and Boomers.
For instance, Gen Z and Millenials have a greater social media presence and are more trend-aware than Boomers. So it makes sense to use social media-heavy marketing strategies rather than emails while targeting them.
Download E-Book : Read more from our Media and Entertainment Master Pack
How To Choose A Customer Segmentation Strategy
Here’s how to find the best customer segmentation model for your business:
1. Collect and organize your customer data
Customer data is the foundation for your segmentation model. Some common examples are personal details, website activities, CSAT scores, customer lifetime value scores, etc.
You can collect valuable customer data and turn them into insights using feedback surveys, running contests, monitoring website traffic, or social listening. The collected customer data can help you create a useful segment to engage with your target audience.
WebEngage’s Customer Data Platform gives you an easy way out of manually collecting and organizing data. Import and collect data by integrating with multiple third-party sources and organizing it into a unified source of truth.
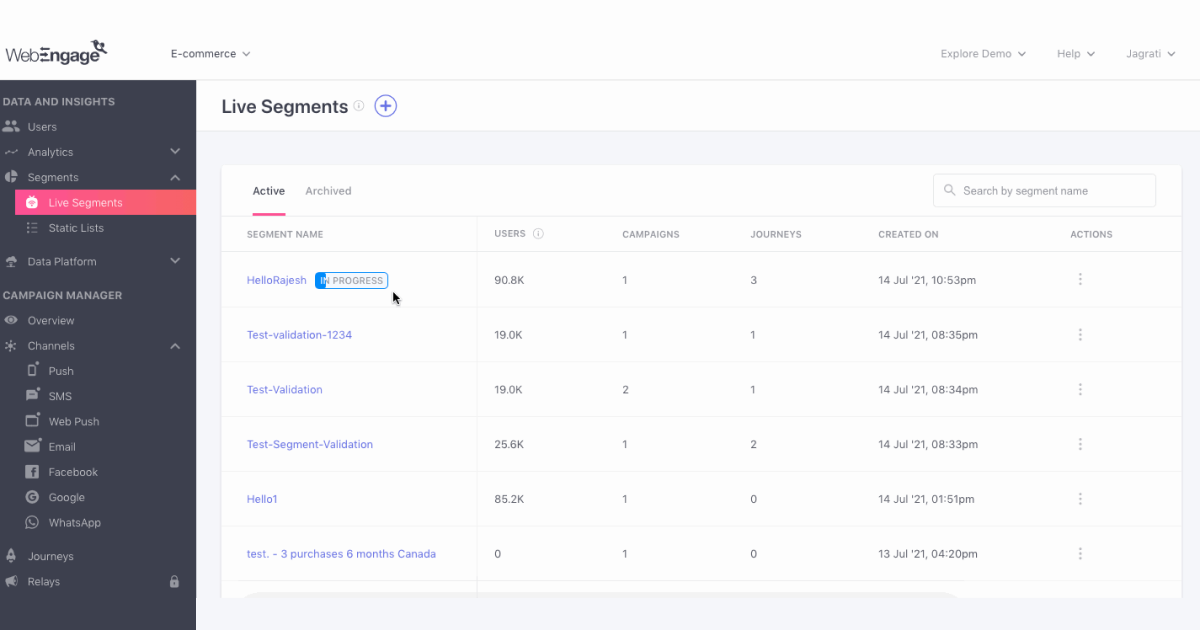
2. Segment your customers into groups of your choice
Now that your customer data is ready, it’s time to segment customers. Here are some tips for doing this:
- Start building segments that are easy to understand since your new segments are used across all teams and departments. Ensure they make sense and are easy to use.
- Build static customer segments using customer attributes, behavioral data, location, interests, and others discussed in the previous section.
- Ensure your segments are segmented generationally, too. For instance, email marketing may suit Gen X but not Gen Z.
- No matter how accurate your segments are, ensure they align with your business goals.
- Analyze and understand how combining two or more segments work synonymously. For instance, using needs-based and demographic segmentation to hyper-target a customer group.
3. Determine your customer segmentation goals and variables
Segmentation aims to tailor the marketing, sales, or support efforts that fit your ideal buyer personas.
And setting segmentation goals can help you create more useful customer segments. Start by analyzing what makes a customer value. Is it the number of repeated purchases they make? Is it the communities they are in? Is it their buyer journeys? Etc.
It’s also crucial to understand the various variables present under every segment.
For instance, you want to market a study table. So demographic and behavioral are your preferred models. You target university students between the ages of 19 to 25. But when are the study table sales higher? It’s either during the start of the academic year or the exam season — which forms the segmentation variables.
As you saw, such variables significantly impact marketing and sales efforts for your chosen segment.
4. Break goals into customer-centric segmentation projects
You now have your customer data, segmentation goals, and variables in place. Next, break them into customer-centric, data-driven segmentation projects.
Such projects let you tackle business goals one step at a time. As you set projects, you will notice that some projects would fetch results faster, like 2x conversions, more engagement, etc., than the rest. Customer-centric projects also let you delegate tasks to multiple teams, choose the right deliverables, and execute smoothly.
5. Set up and prioritize each customer segmentation project
Once you’ve identified segmentation projects, it’s time to set them up and prioritize them based on their potential impact on your business.
How can you prioritize projects?
Consider factors such as the size of the segment (number of customers present) or their performance, like purchasing power. Once sorted based on these factors, it’s time to set up projects:
- Set an objective, for example, sending a product launch notification to your existing customers from a particular demographic.
- To avoid data or knowledge silos, involve multiple stakeholders like teams, loyal customers, vendors, etc., to convey their role in the project.
- Define the project scope (resources, cost, data sources, customer needs) to avoid future surprises.
- Finally, clearly define the results your project is expected to achieve.
6. Target and market to your client and user segments
Your customer segments are ready, and it’s time to put them into action. Here are two simple ways to achieve the most out of your created segments:
Your communication must feel genuine. Create customer-centric content that customers can engage and resonate with. Also, make sure you’re not sending similar messaging to different segments.
Create a unique stepwise plan for each segment to ensure no two segments are alike.
7. Run regular customer segmentation analysis
Data is ever-changing, and so are your customer segments. Real-time analytics is what you need to ensure your customer segments stay useful.
Run customer segmentation analyses and review them regularly to keep up with their performance.
Features from the WebEngage dashboard that aid in segmentation
1. Live segmentation
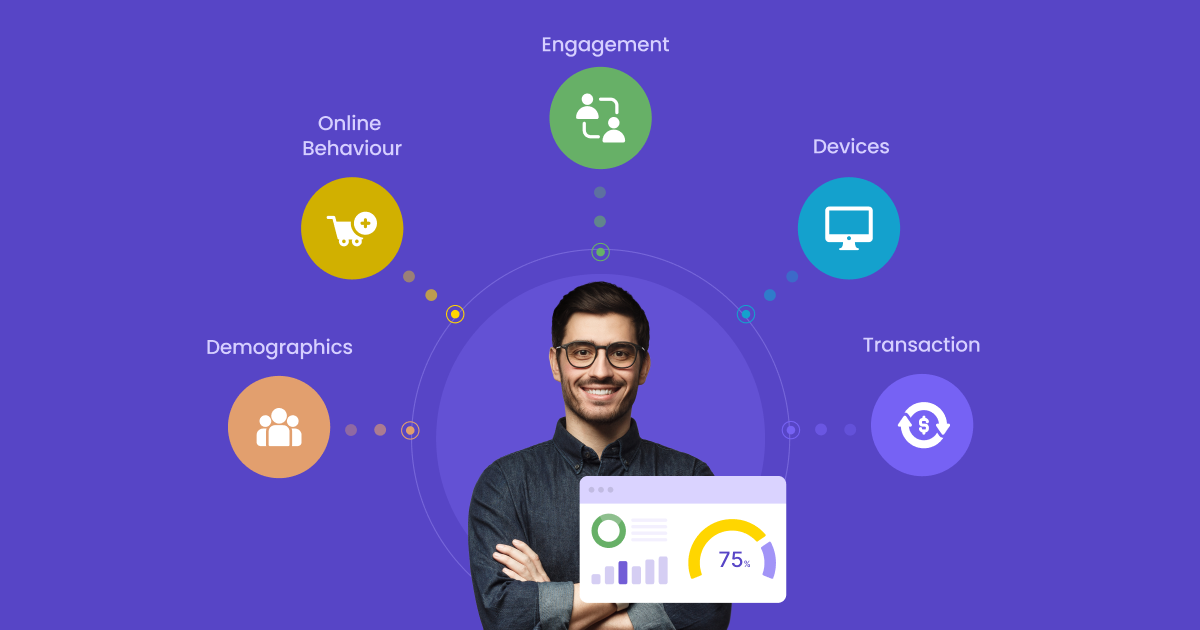
Live segmentation is when you analyze your customers for a long period and define their traits to create Live Segments.
Your traits could be business-specific, like age group, location, purchase history, preferences, wishlist products, etc.
WebEngage lets you specify each trait as a segmentation rule to build your Live Segment.
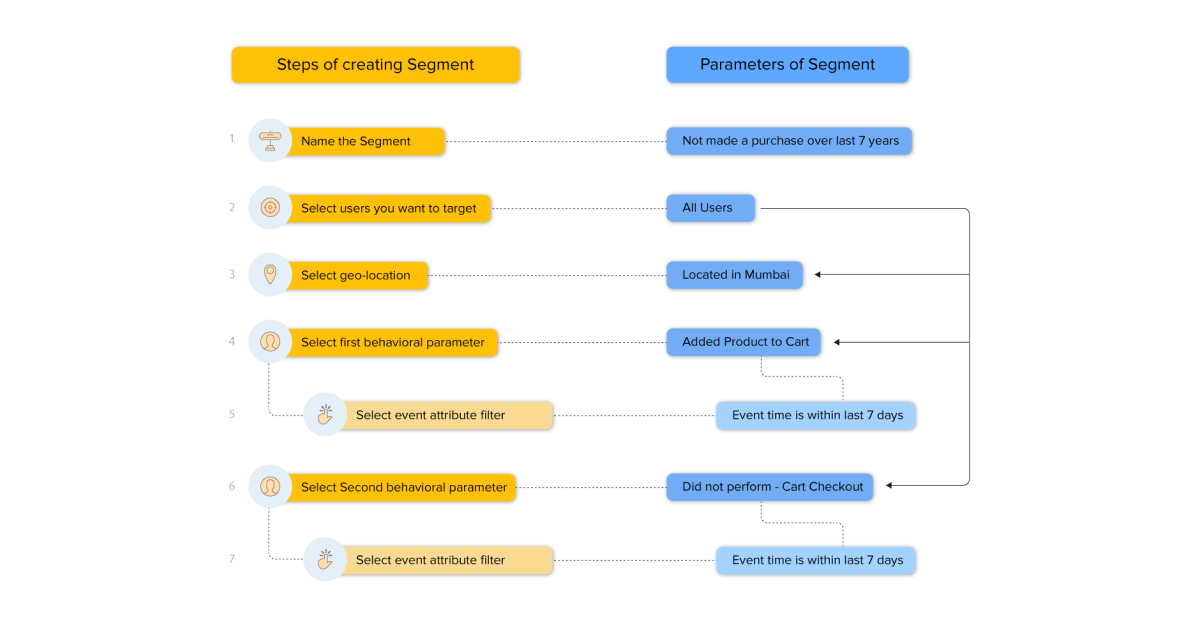
Here are some benefits of using Live Segments:
- Delivering contextually personalized user experiences at various customer life cycle stages.
- Personalized content based on customers’ unique traits.
- Better monitoring and responding to changing customer preferences.
2. Predictive segmentation
This type of high-level segmentation is when you identify and separate user clusters programmatically or by using machine learning methods. It can also be called an AI-based or data-driven segmentation model.
Here’s how you can perform predictive segmentation using machine learning using WebEngage:
- Clustering algorithms — A good starting point for data-driven segmentation. This is an unsupervised machine learning technique where you group segments together based on shared characteristics.
- Classification — This supervised machine learning technology helps you predict outcomes based on features, in our case, pages visited, device types, etc.
- Experimentation — Performing controlled experimentation on high-potential segments and using a tool like WebEngage that helps detect lucrative segments automatically.
3. Static lists
Static lists are stagnant user pools created to send one-off campaigns for smaller customer groups. The evolving users’ preferences or traits do not affect these static groups.
Static lists of user groups are useful when running one-off campaigns to invoke immediate action like conversions, user activation, or conveying a particular message.
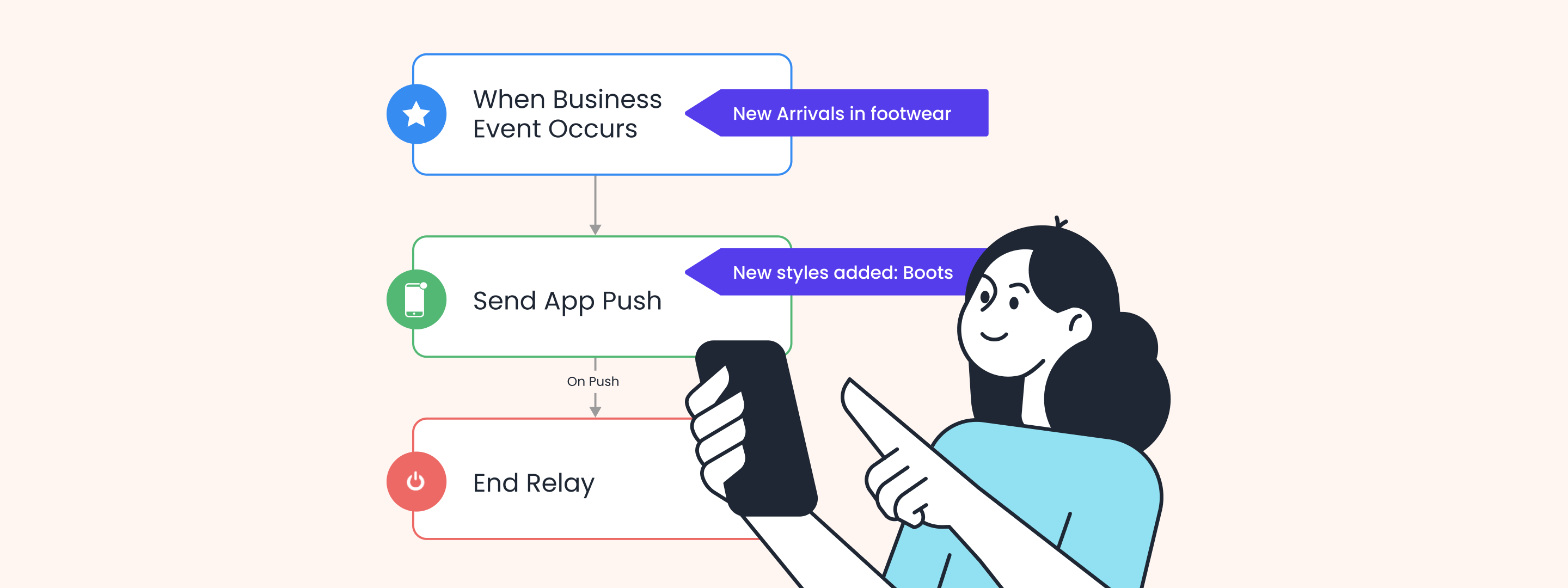
Know more about 4 best behavioral segmentation practices
Conclusion
No matter your chosen segmentation model, it needs to adapt to your business objective. And the secret behind laser-focused customer segmentation is data.
You first need to have data from all channels in a single, unified source. That’s where WebEngage teps in.





 Ananya Nigam
Ananya Nigam
 Prakhya Nair
Prakhya Nair

 Diksha Dwivedi
Diksha Dwivedi
 Inioluwa Ademuwagun
Inioluwa Ademuwagun